Projekt: Kidney - Kidney anatomy
Skrýt detaily | Oblíbený- Kvalita:88,2 %
- Typ:Projekt
- Univerzita:Univerzita Karlova v Praze
- Fakulta:3. lékařská fakulta
- Kategorie:Přírodní vědy
- Podkategorie:Zdravotnictví, lékařství
- Předmět:Fyziologie
- Autor:josef.trousil
- Ročník:1. ročník
- Rozsah A4:42 strán
- Zobrazeno:1 875 x
- Stažené:0 x
- Velikost:0,2 MB
- Formát a přípona:MS Office Word (.doc)
- Jazyk:anglický
- ID projektu:3376
- Poslední úprava:19.05.2014
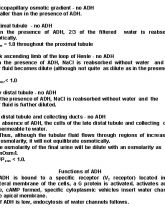
KIDNEY ANATOMY
Pelvis
Cortex
Medulla:
outer medulla subdivides into an outer and inner stripe
Inner medulla has papillae (tips) -> minor calyx -> major calyx
Renal artery is subdivided into interlobar arteries -> arcuate artery -> cortical radial artery ->afferent arteriole ->glomerular capillary network -> efferent arteriole ->peritubular capillary network
Nephrons and are the functional units of the kidney
They are superficial and juxtamedullary
Renal corpuscle: glomerulus plus Bowman's capsule
The superficial nephron has a short loop of Henle that reaches into the outer medulla. Its efferent arteriole branches into the peritubular capillary network that surrounds the tubular segments of the same and other nephrons.
The juxtamedullary nephron arises from the deep cortical regions, next to the medulla, glomerulus is larger than that of the superficial nephron, its loop of Henle reaches into the inner medulla. Its efferent arterioles form peritubular capillary network and vasa recta. Vasa recta break into capillaries surrounding collecting ducts and the loops of Henle.
Heterogeneity of nephrons
Their heterogeneity is due to several various subdivisions of tubules and several types of cells in the tubules. There are different types of microvilli at the luminal surfaces, different number of mitochondria, different number of basal infoldings.
Juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA)
It is formed by specialized epithelial cells in the thick ascending limb (the macula densa cells), lacis cells, and by secretory cells at the vascular pole where the afferent and efferent arterioles meet. JGA secretes renin.
Pelvis
Cortex
Medulla:
outer medulla subdivides into an outer and inner stripe
Inner medulla has papillae (tips) -> minor calyx -> major calyx
Renal artery is subdivided into interlobar arteries -> arcuate artery -> cortical radial artery ->afferent arteriole ->glomerular capillary network -> efferent arteriole ->peritubular capillary network
Nephrons and are the functional units of the kidney
They are superficial and juxtamedullary
Renal corpuscle: glomerulus plus Bowman's capsule
The superficial nephron has a short loop of Henle that reaches into the outer medulla. Its efferent arteriole branches into the peritubular capillary network that surrounds the tubular segments of the same and other nephrons.
The juxtamedullary nephron arises from the deep cortical regions, next to the medulla, glomerulus is larger than that of the superficial nephron, its loop of Henle reaches into the inner medulla. Its efferent arterioles form peritubular capillary network and vasa recta. Vasa recta break into capillaries surrounding collecting ducts and the loops of Henle.
Heterogeneity of nephrons
Their heterogeneity is due to several various subdivisions of tubules and several types of cells in the tubules. There are different types of microvilli at the luminal surfaces, different number of mitochondria, different number of basal infoldings.
Juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA)
It is formed by specialized epithelial cells in the thick ascending limb (the macula densa cells), lacis cells, and by secretory cells at the vascular pole where the afferent and efferent arterioles meet. JGA secretes renin.